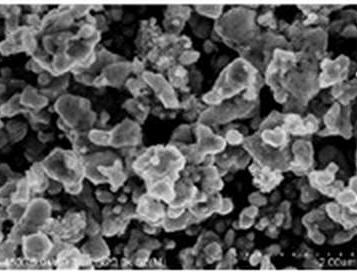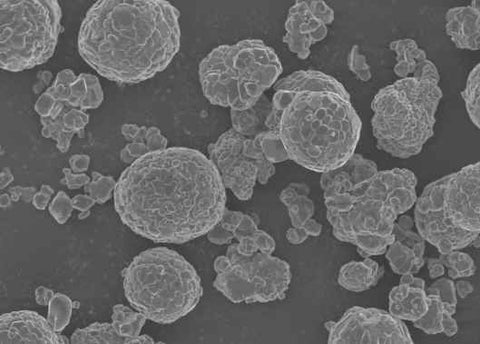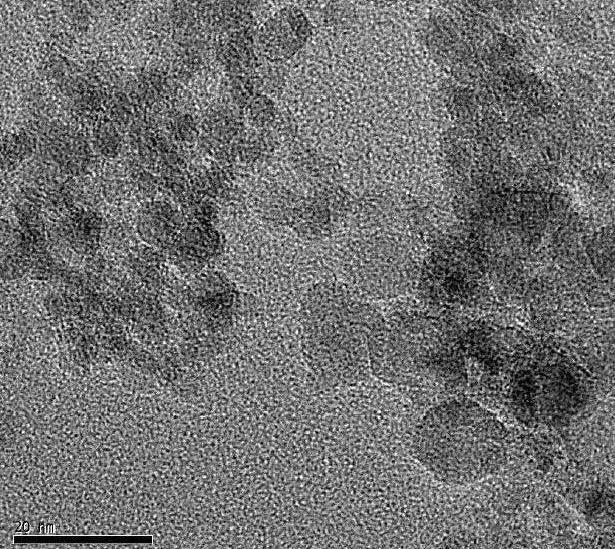
Diamond Nanoparticles
Diameter: ~5nm, 40nm and 90nm. 4 to 15nm is also available
Appearance: powder
Growth method: detonation method
Dispersions of nanodiamond in various solvents are also available, please contact us at info@novarials.com
Select Applications of Nanodiamonds
(1) Adsorption of Biomolecules
Nanodiamonds, due to their large surface area, chemical stability, and abundant surface functional groups, play an increasingly important role in the field of biomedicine. They achieve adsorption of small and large biomolecules through hydrophilic/hydrophobic interactions and electrostatic forces, contributing to drug delivery, cancer treatment, protein separation, sterilization, and other medical applications.
The gene delivery platform based on nanodiamonds is a convenient, rapid, and versatile tool for gene transfer. Modified nanodiamonds, through electrostatic interactions, exhibit high affinity for nucleic acids, facilitating gene transport to the cell nucleus, enhancing disease treatment capabilities, and demonstrating low cytotoxicity. Therefore, nanodiamonds as gene carriers for targeted therapy present a promising approach in disease treatment.
(2) Biosensing
Fluorescent nanodiamonds, characterized by high photostability, bright multicolor fluorescence, low biological toxicity, and stable physicochemical properties, hold valuable applications in biosensing. Organic fluorescence probes, when exposed to intense light sources, tend to bleach, unlike nanodiamonds that remain unaffected even under strong illumination. Nanodiamonds are employed in detecting important signaling molecules during cell growth, such as hydrogen peroxide, glutathione, and metal ions, providing reliable tools for biosensing, cell tracking, and exploring cellular activities.
(3) Cell Labeling and Biomedical Imaging
High-energy particle irradiation of nanodiamonds under high temperature and pressure, followed by high-temperature annealing, can generate nitrogen-vacancy (NV) color centers, imparting fluorescence to nanodiamonds. These fluorescent nanodiamonds are suitable for biomedical imaging. Negatively charged NV color centers in diamond exhibit broad red emission (600-800 nm) with excellent photostability, making them well-suited for biological imaging within the tissue transparency window. Although the excitation wavelength typically falls within 510-560 nm, absorbing organic molecules, leading to tissue autofluorescence interference and limited tissue penetration, surface modification with fluorescent groups on smaller nanodiamonds below 50 nm can enhance their fluorescence performance.
(4) Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering involves the construction of biocompatible tissue substitutes to restore and improve tissue function. Nanodiamonds, possessing good biocompatibility and antibacterial properties, offer an alternative to traditional materials in tissue engineering applications. Unlike traditional metallic coating materials that may induce metal allergies and rejection reactions, nanodiamonds do not cause immune rejection. Additionally, joint materials manufactured from nanodiamonds exhibit minimal wear compared to traditional metal materials. Nanodiamonds also show promise as dental materials.